
Simple Guide: Checking Chromebook Specs and Usage for Peak Performance
Is your Chromebook feeling sluggish? Want to understand its capabilities better? This guide provides easy steps to check your Chromebook's CPU usage, RAM, storage, and more, helping you optimize its performance and understand its hardware. Let's dive in!

Monitor CPU Usage on Your Chromebook
If your Chromebook is running slowly, identifying which applications are using the most processing power can help. Check CPU usage through these simple steps:
-
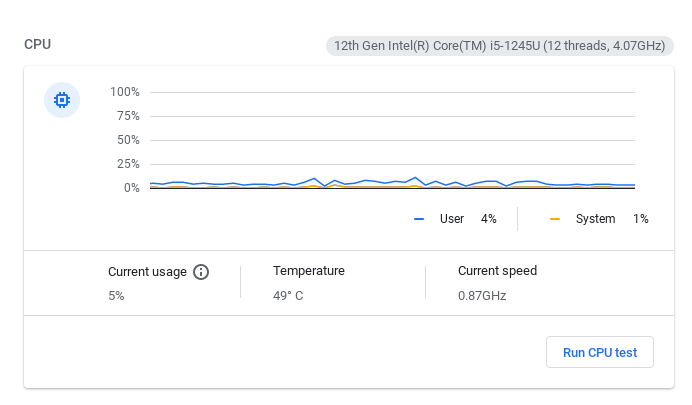
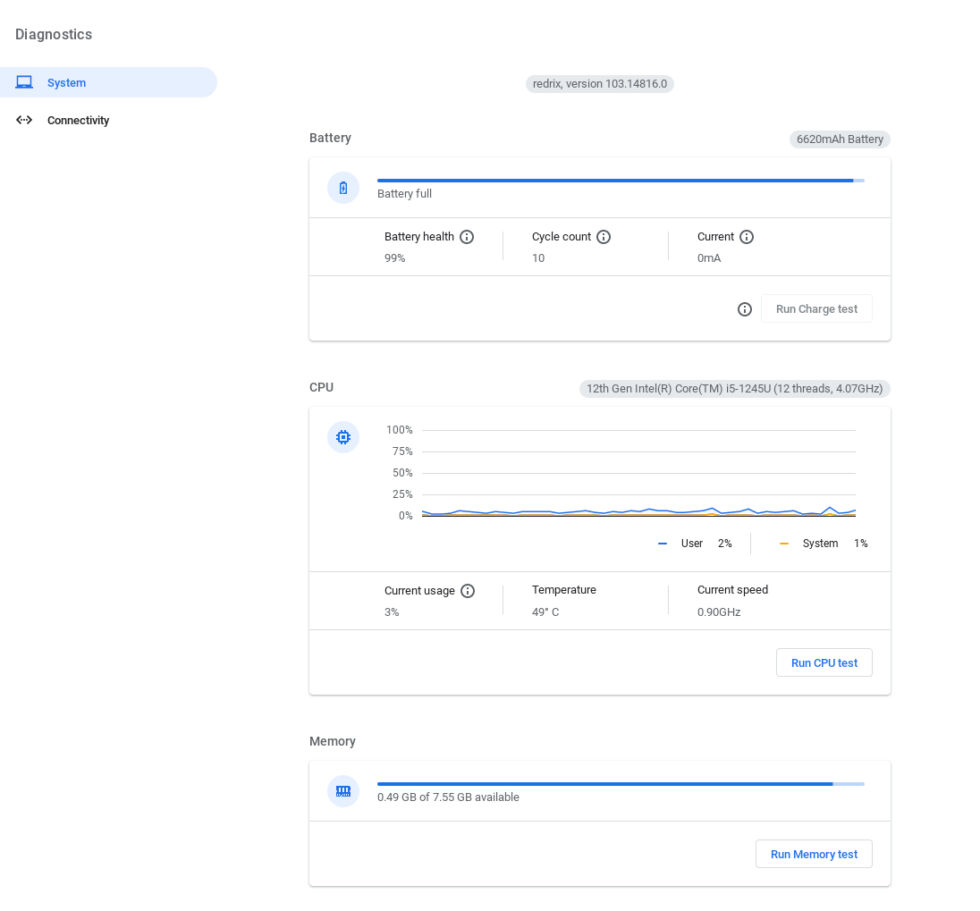
Diagnostics Page: Type "Diagnostics" in the ChromeOS search bar. The Diagnostics page displays a live graph of CPU usage, temperature, and current speed.
-
ChromeOS Task Manager: Press Search + Esc to open the Task Manager, providing insights into CPU, memory, and network usage. Alternatively, access it via Chrome's three-dot menu -> More tools -> Task Manager.
The Task Manager shows you exactly which processes are hogging resources, allowing you to close unnecessary apps and browser tabs.
Enable or Disable Hyper-Threading for Enhanced Performance
Hyper-threading, available on some Intel Chromebooks, can improve performance by allowing a single processor core to act as two virtual cores. However, it's often disabled due to security concerns.
**How to enable Hyper-threading (at your own risk): **
- Ensure you're running Chrome OS 74 or later.
- Type
chrome://flags#scheduler-configurationin the Chrome browser. - Change the "Scheduler Configuration" setting from "Default" to "Enables Hyper-threading on relevant CPUs."
- Restart your Chromebook.
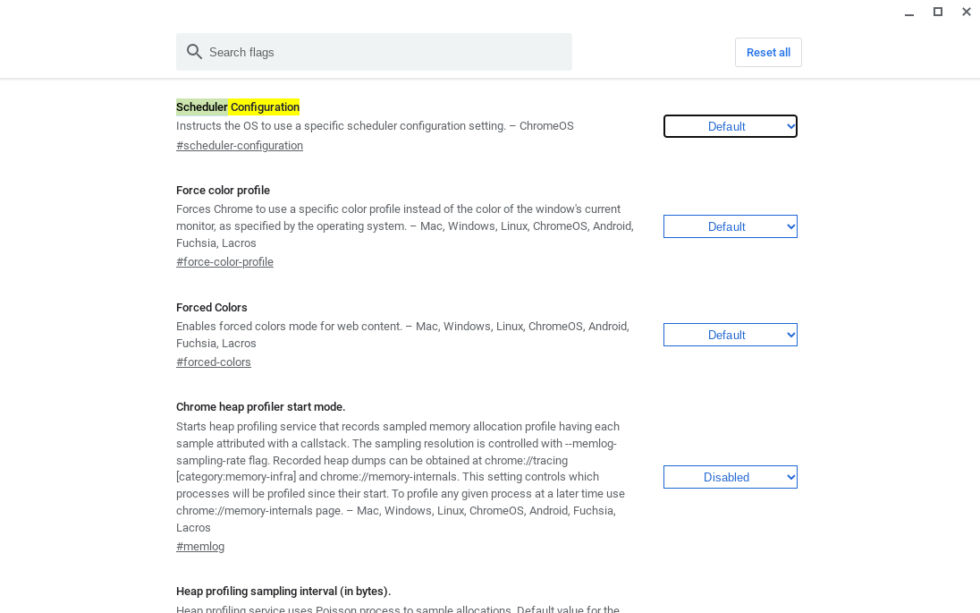
Consider the security implications before enabling this feature, especially on work devices.
Use GPU Rasterization to Boost Performance
GPU rasterization shifts workload from the CPU to the GPU, potentially improving performance, but may reduce battery life. Enable it via chrome://flags:
- Type
chrome://flagsin the Chrome browser. - Search for "GPU rasterization."
- Enable the feature and restart your Chromebook.
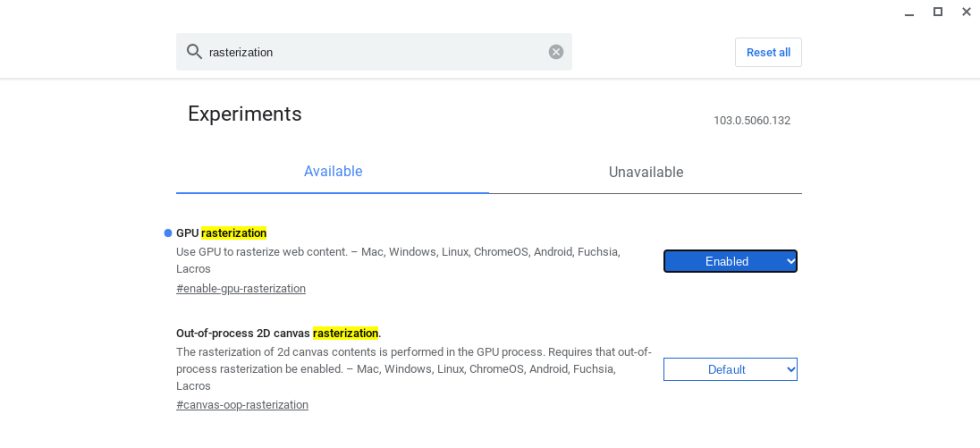
Experiment to see if this improves your Chromebook's responsiveness.
Find Your Chromebook's CPU Model
Knowing your Chromebook's CPU helps when troubleshooting or comparing its performance. Here's how to find it:
Diagnostic Page:* As mentioned earlier, the Diagnostics page (accessed via search or Settings -> About ChromeOS -> Diagnostics) displays your CPU model and thread count.
Chrome://System Page:* Type chrome://system in the Chrome browser and expand the "cpuinfo" section. This reveals the processor name and other details like cache size.
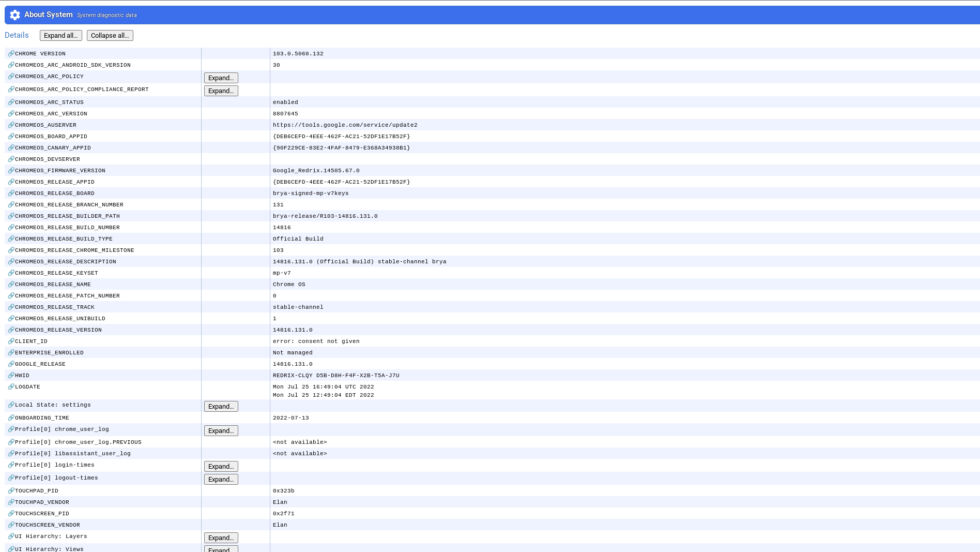
Digging into the chrome://system page provides extensive hardware information.
Determine RAM Usage for Smooth Multitasking
High RAM usage can cause slowdowns. Monitor RAM usage in the Task Manager (Search + Esc) to identify memory-intensive processes.
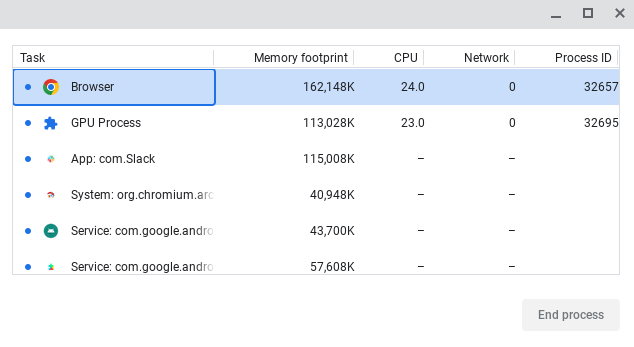
Consider using tab management extensions like OneTab or The Great Suspender to conserve memory by suspending unused tabs. Always verify the safety of extensions before installing them.
Check Total and Available RAM
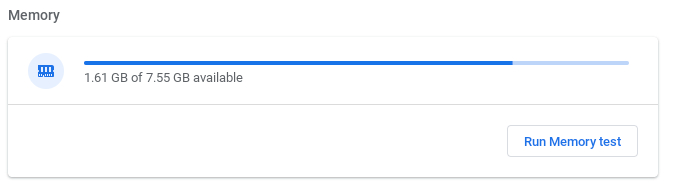
Knowing your Chromebook's total RAM helps you understand its multitasking capabilities. Find this information on the Diagnostics page.
Type "Diagnostics" in the ChromeOS search bar to find total and available RAM.
Discover Your Chromebook's Storage Type
Chromebooks use various storage types, like SSDs or eMMC. To find out what type your Chromebook uses:
- Type
chrome://systeminto Chrome's address bar. - Scroll to "storage_info" and click "Expand...".
- Search the storage model name online to learn more about its specifications.
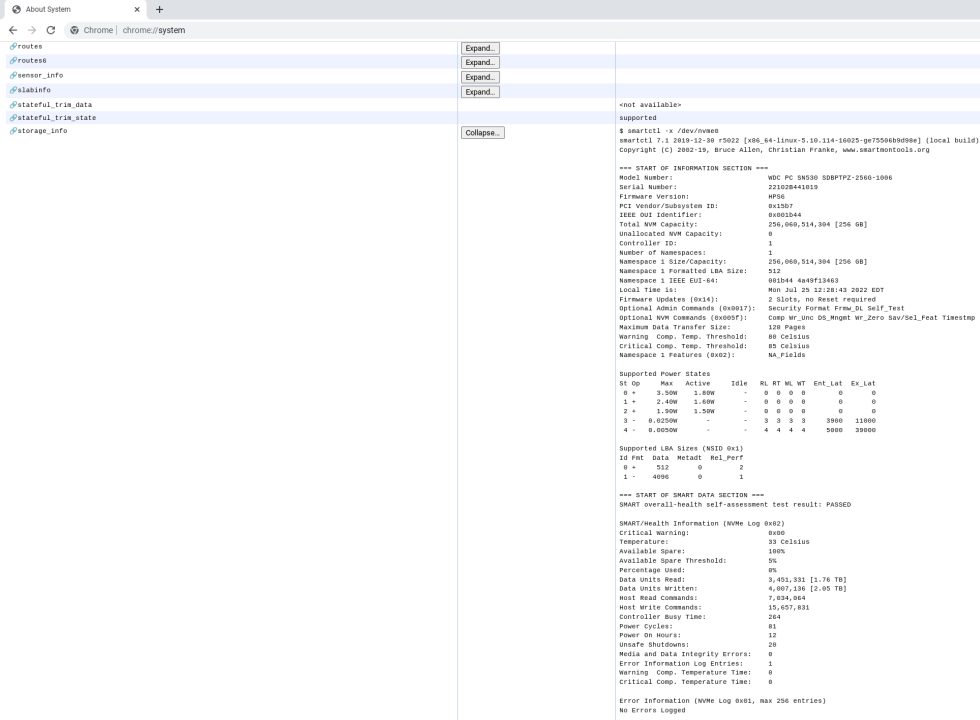
Knowing the storage type can help you understand its performance characteristics.
Find Available Storage Space
Quickly check available storage via Storage Management in ChromeOS settings:
- Search for "storage" in the ChromeOS search bar and select "Storage Management."
- Alternatively, go to Settings -> Device -> Storage Management.
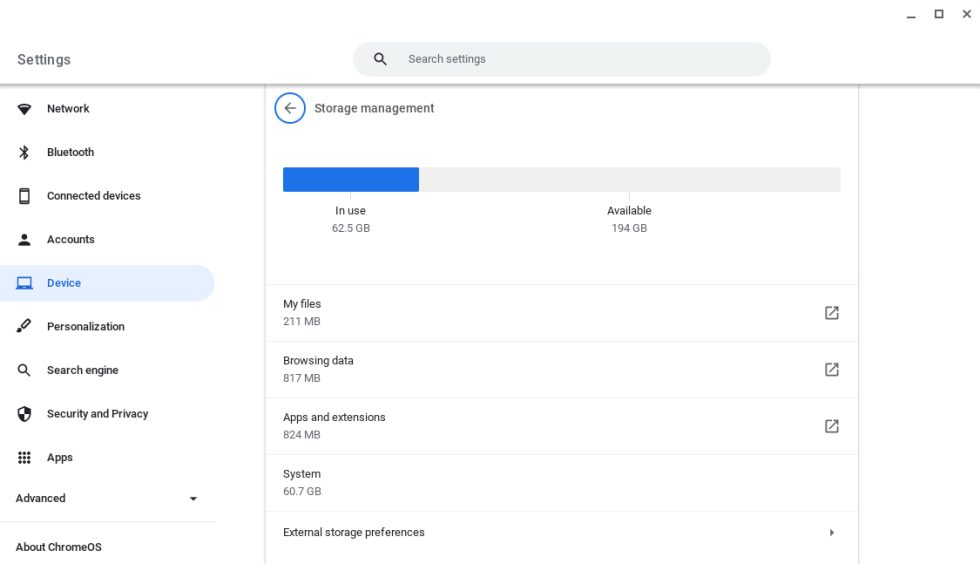
This page shows total storage, used space, and remaining space. Understanding your Chromebook's specifications and resource usage ensures optimal performance and helps you make informed decisions about apps, files, and usage habits.






